Common Kingfisher Health Issues: How to Identify and Help These Birds
The Common Kingfisher, with its vibrant colours and agile hunting skills, plays an important role in our ecosystems. However, these beautiful birds face various health challenges that can impact their survival. Understanding these issues is essential for anyone who loves wildlife or engages in conservation efforts.
In this post, you’ll learn how to identify common health problems in kingfishers and the steps you can take to help them. From recognising signs of distress to knowing when to seek professional assistance, this guide provides useful insights for bird enthusiasts and nature lovers. By addressing these health issues, we can ensure that the Common Kingfisher continues to thrive in our environment.
Common Health Problems in Kingfishers
Like any wildlife, kingfishers can experience a range of health issues. Understanding these problems is essential for wildlife enthusiasts and conservation efforts. Here’s a look at some common health problems affecting these beautiful birds:
Infectious Diseases
One significant threat to kingfishers is infectious diseases, particularly Chlamydiosis. This bacterial infection often shows symptoms such as:
- Respiratory issues: Sneezing and coughing.
- Digestive problems: Diarrhoea or dark green droppings.
- Behavioural changes: Poor feeding habits and lethargy.
If you notice these signs, it’s crucial to seek help from a wildlife rehabilitator or veterinarian. For more detailed information on chlamydiosis in birds, refer to the NSW Health page.
Nutritional Deficiencies
Kingfishers need a balanced diet to stay healthy. Nutritional deficiencies can lead to various health problems, including:
- Vitamin A deficiency: Can cause poor feathering and eye issues.
- Calcium deficiency: Essential for proper bone and egg development.
- Protein deficiencies: May lead to stunted growth and weakened immunity.
Ensuring kingfishers have access to a rich diet full of aquatic life is vital. You can learn more about nutritional disorders in birds from the Merck Veterinary Manual.
Parasitic Infestations
Kingfishers are also susceptible to various parasites, such as mites, worms, and protozoa. These parasites can affect their health by:
- Causing weight loss and anemia.
- Leading to skin irritations or feather loss.
- Compromising the bird’s immune system.
Regular health checks and a clean habitat can help in the prevention of these infestations. For more details, check this resource on common avian parasites.
Environmental Stressors
Environmental changes can significantly impact kingfisher health. Factors such as climate change and habitat loss pose severe threats. Some notable stressors include:
- Pollution: Contaminants in water can lead to various diseases.
- Noise pollution: Increased noise can cause chronic stress in birds, affecting their behaviour and breeding.
Understanding these stressors is essential for any conservation effort aimed at protecting kingfishers. You can read about the effects of pollution on wildlife in this ScienceDirect article.
Injuries and Accidents
Kingfishers are prone to injuries from various accidents. Common causes include:
- Window collisions: Birds may not see glass and can suffer severe injuries.
- Predation: Threats from larger birds or mammals can result in physical harm.
- Fishing accidents: Hooks and nets can entrap or injure them.
If you find an injured kingfisher, it’s critical to contact a wildlife rehabilitation centre for assistance. For example, read about a case involving an injured kingfisher here.

Photo by Pixabay
Signs of Illness in Kingfishers
Recognising when a Common Kingfisher is unwell can be challenging but essential for providing timely assistance. Observing their behaviour and physical condition can help in identifying health issues early on. Below are key signs of illness to look out for.
Behavioural Changes
Changes in behaviour are often the first signs that something is amiss. Healthy kingfishers are active and inquisitive, but illness can lead to noticeable shifts. Some common behavioural changes include:
- Lethargy: If a kingfisher is less active than usual or sleeps more, this is a red flag.
- Loss of appetite: A disinterest in feeding can indicate a health issue.
- Isolation: If the bird seems to avoid social interactions or hides away, it’s a cause for concern.
- Abnormal vocalisation: Changes in their singing or calling can signal distress.
It’s important to monitor these behaviours closely. For further details on recognising illness in birds, check out the resource by LafeberVet.
Physical Symptoms
In addition to behavioural changes, physical signs can provide critical insights into a kingfisher’s health. Key physical symptoms to be aware of include:
- Feather loss or poor plumage: Tattered or missing feathers may suggest stress or illness.
- Weight loss: Noticeable thinning can indicate a severe problem.
- Fluffed feathers: This often means the bird is trying to maintain body heat due to illness.
- Abnormal droppings: Changes in the colour, consistency, or frequency of droppings can point to digestive issues.
Being vigilant about these physical indicators can aid in ensuring the bird receives the necessary care. For more common health issues, refer to this resource.
Seeking Professional Help
Knowing when to seek help is crucial. If you observe any signs of illness in a kingfisher, contacting a professional should be a priority. Here are some guidelines for when to reach out:
- Persistent symptoms: If you notice behavioural or physical symptoms lasting more than a day or two, it’s time to consult a vet or wildlife rehabilitator.
- Severe injuries: Any physical trauma, such as broken wings or major feather loss due to predation, requires immediate attention.
- Infections or infestations: Signs of respiratory distress, unusual discharges, or visible parasites need urgent care.
Wildlife rehabilitators and vets have the expertise to assess and treat kingfishers effectively. For more detailed guidance on when to consult a professional, visit this page about common conditions of pet birds.
Photo by Anna Shvets
How to Help Common Kingfishers
Supporting the health and wellbeing of Common Kingfishers involves several proactive steps. By creating suitable habitats, ensuring proper nutrition, reporting injured birds, and fostering community involvement, we can make a significant difference in the lives of these beautiful birds.
Creating a Suitable Habitat
Providing an optimal habitat is essential for the health of Kingfishers. Here are some ways to create a supportive environment:
- Nest Banks: Kingfishers prefer to nest in vertical mud banks at least three feet high. If you have a suitable bank on your property, consider maintaining its natural state.
- Water Sources: Make sure there are clean, shallow waters nearby. Kingfishers thrive near rivers, lakes, and ponds teeming with fish and aquatic invertebrates.
- Vegetation: Plant native shrubs and trees that provide shelter. This will not only attract kingfishers but also offer other wildlife refuge.
For further insights on building a suitable habitat, read about challenges kingfishers face and how to help.
Feeding and Nutrition Guidelines
Proper nutrition is crucial for Kingfishers in care. Key dietary considerations include:
- Aquatic Prey: Provide small fish, insects, and crustaceans, which form the bulk of their natural diet.
- Variety: Offer an assortment of protein sources. This could include worms, frogs, and even small mammals.
- Hydration: Ensure they have access to clean water at all times. This is critical for their health and wellbeing.
For specific feeding guidelines, check the feeding habits of kingfishers.
Reporting Injured Birds
If you encounter an injured Kingfisher, it’s vital to take the right steps:
- Assessment: Evaluate the bird for visible injuries. Look for broken wings, bleeding, or signs of distress.
- Contact Professionals: Reach out to wildlife rehabilitation centres or local animal control for guidance and assistance. They have trained staff to provide support.
- Avoid Handling: If possible, leave the bird alone unless it is in immediate danger. Handling can cause further stress.
For more details about reporting injured wildlife, refer to the U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service’s guide on sick or injured wildlife.
Community Involvement
Community initiatives play a significant role in protecting Kingfishers. Here are ways you can get involved:
- Awareness Campaigns: Participate in local conservation efforts focused on educating the public about Kingfishers and their habitats.
- Clean-up Drives: Join or organise clean-ups around water bodies to reduce pollution and keep habitats clean for wildlife.
- Volunteer: Support local wildlife rehab centres by volunteering your time or resources. Every bit helps!
Connecting with others in your community can amplify these efforts. For more on community conservation initiatives, check out this page about conservation efforts for kingfishers.
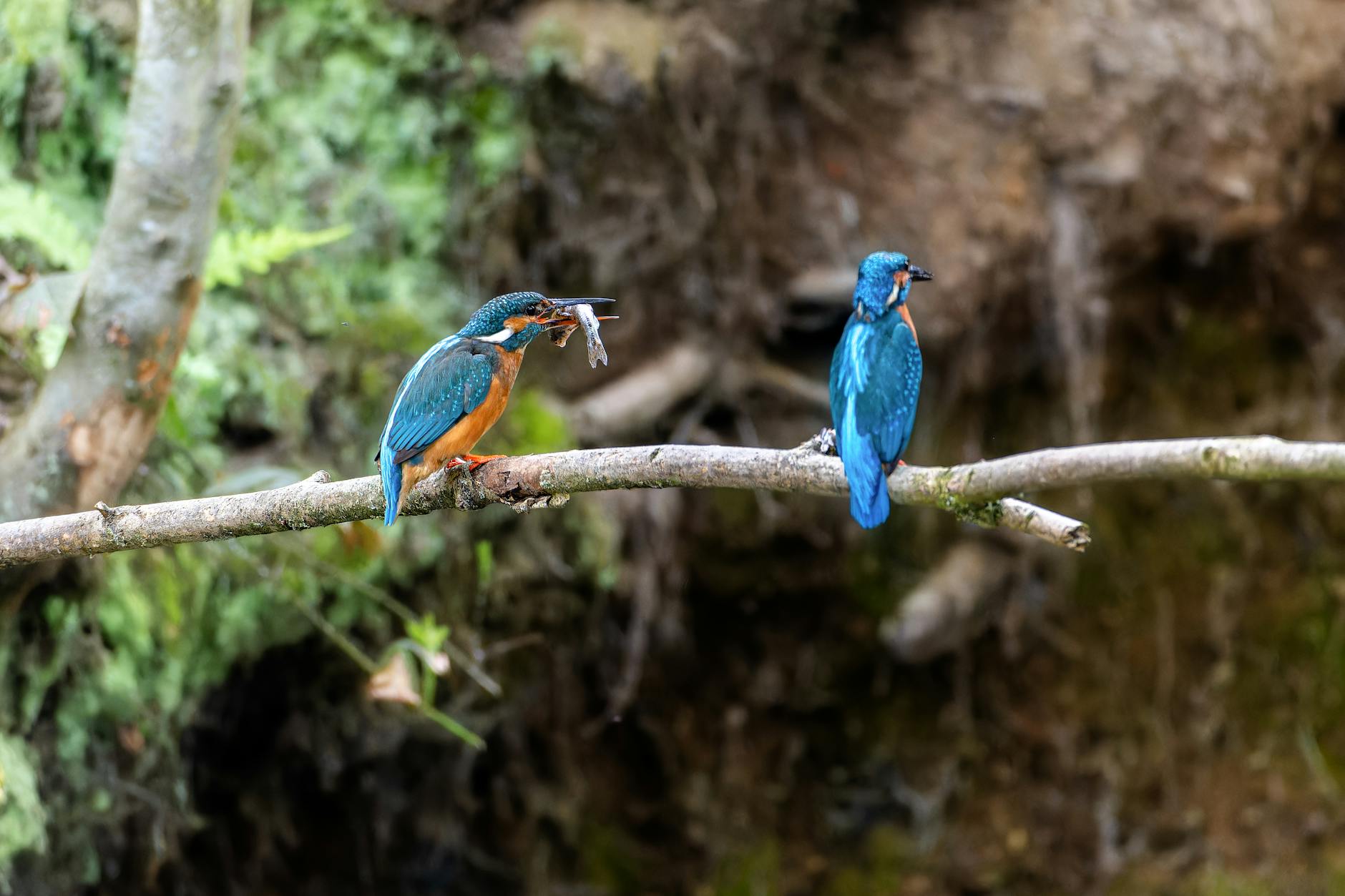

Photo by Siegfried Poepperl
Conclusion
Addressing the health issues affecting Common Kingfishers is critical for their survival and wellbeing. Recognising and acting upon these problems ensures that these stunning birds continue to thrive in our ecosystems.
Importance of Addressing Health Issues
When we talk about the health of Kingfishers, we touch upon our responsibility as stewards of nature. Ignoring their health issues could lead to population declines, which can disrupt local ecosystems. Here are some key reasons why addressing their health is important:
- Biodiversity: Healthy Kingfishers contribute to the biodiversity of their habitats, which is essential for ecological balance.
- Indicator Species: Their health often reflects environmental quality. Monitoring Kingfisher health can indicate broader ecosystem issues.
- Conservation Efforts: By understanding and mitigating health risks, we can enhance conservation strategies and create more effective intervention plans.
For an in-depth look at the health management of Kingfishers, take a look at this Guam Kingfisher Health Overview.
Encouraging Ongoing Support
Supporting Common Kingfishers requires a concerted effort from individuals and communities. Get involved by:
- Educating Yourself and Others: Share knowledge about Kingfisher health and conservation needs.
- Participating in Community Projects: Join local initiatives that promote habitat preservation and pollution reduction.
- Reporting Findings: If you notice a sick or injured Kingfisher, report it to local wildlife authorities or rehabilitation centres.
Every action counts. Together, we can ensure a healthier future for Common Kingfishers. Learn how to help these birds by visiting WikiHow’s guide on attracting Kingfishers.

Photo by Siegfried Poepperl










